As the core diameter of this fiber is important; the fiber behaves like a multimode fiber; the light rays injected will follow different paths according to their angles of incidence in the fiber. We also define the numerical aperture of the fiber which characterizes the maximum angle of light input into the fiber through the light can be guided.
The, majority of polymer optical fibers are step-index profile, that is to say that the core has a refractive index nc and the cladding has a refractive index ng lower than the refractive index of the core nc. The PMMA refractive index is around 1.49. The digital aperture of polymer optical fiber is calculated from a theoretical point of view by
sinӨmax =√(nc2- ng2 )
Like any optical fiber in general, polymer optical fiber resists any electromagnetic disturbance. Its big advantage compared to silica-based optical fiber is that it is very simple to handle, in particular thanks to large diameters (dia 1mm as standard), a PMMA material versus silica. Indeed, the connectorization or the implementation of ferrules at the end of the fiber does not involve any great difficulty. This fiber is robust, it resists twists,vibrations and supports small radii of curvature unlike an optical fiber based on silica.
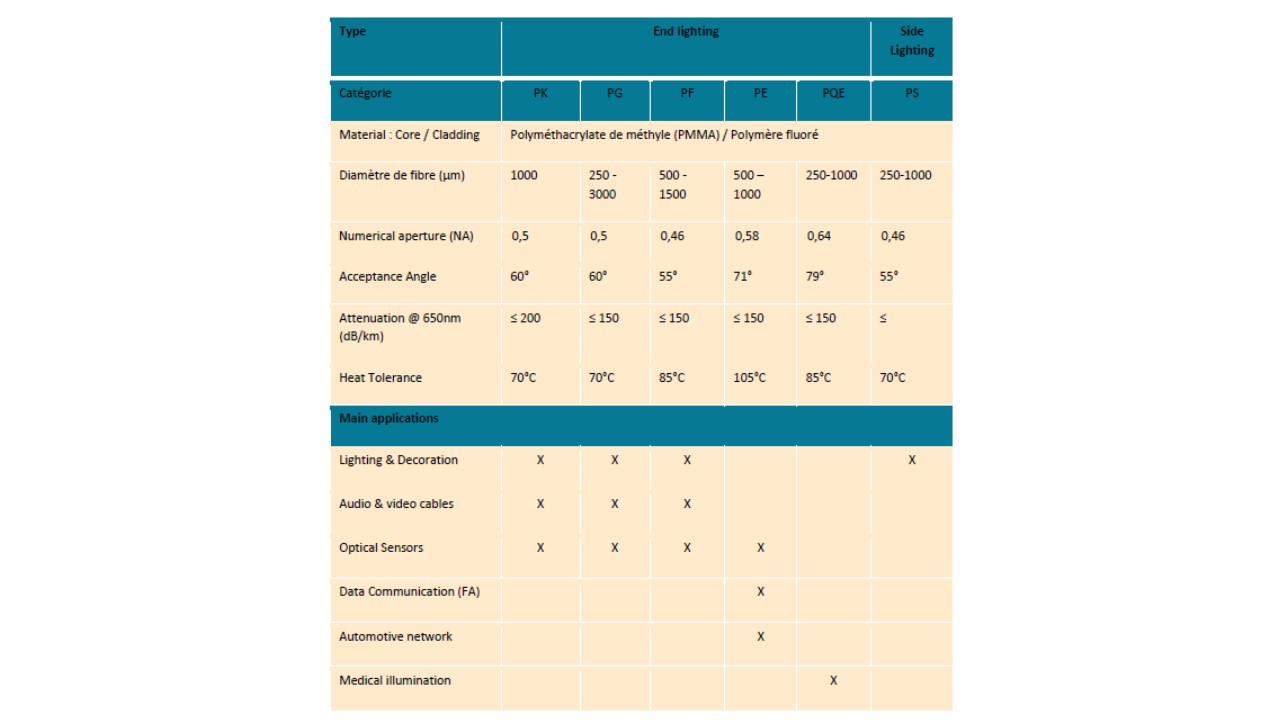
Categorization of polymer optical fiber
The Japanese company, leader in the manufacture of plastic optical fibers,has segmented its offer with several levels of quality in line with the type of application, the operating temperature of the fiber, its numerical aperture.Fiber diameters can vary from 250µm to 3mm. Depending on usage,Toay has segmented its offer into bare fibers(only PMMA core and cladding) simplex or duplex cords (1 or 2 fibers covered with a mechanical polyethylene jacket), cables with double mechanicalprotection above the core and cladding, optical guides with several fibers covered with a mechanical sheath. The table below shows the segmentation made by Toray on plastic optical fibers.